AS400 applications are under growing pressure to keep up with today’s business demands. The 2025 IBM i Marketplace Survey by Fortra reveals that 57% of IBM i users identified application modernization as a top IT priority, 77% expressed concern over cybersecurity risks from outdated protocols, and 60% reported shortages of skilled IBM i professionals, making IBM i modernization a growing necessity.
People are concerned about how to maintain and get along with this “old guy”. Sure, his experience and processes are undeniable (still desirable).
But the combination of rising maintenance costs, an aging talent pool, and increasing security and compliance requirements is forcing organizations to rethink how.
In this guide, we’ll explore the business drivers behind AS400 application modernization, the tangible benefits for operations and growth, and proven strategies for executing a successful transformation.
What We Hear from Clients Every Day?
When organizations come to us about their AS400 applications, the conversation almost always starts the same way.
It’s not about “technology upgrades”, it’s about frustration. It’s about how a system that once ran the business is now slowing it down.
“Our AS400 software is throwing frequent errors during batch processing, affecting inventory updates.”
“Most of the people who built this system are retired… no one knows all the logic anymore. And young programmers don't want to work on AS400”
“We can’t connect it easily to modern platforms, every integration feels like a custom hack.”
Our teams stick with AS400 because they know it well, but they resist moving to anything new. Without the right people to guide them, change management is tough, and modernization feels like a heavy lift.
“We’re worried about compliance and security, but updating the system is complex and expensive.”
We’ve seen this across retail, healthcare supply chains, finance, and logistics. Different industries, but the same core pain points..
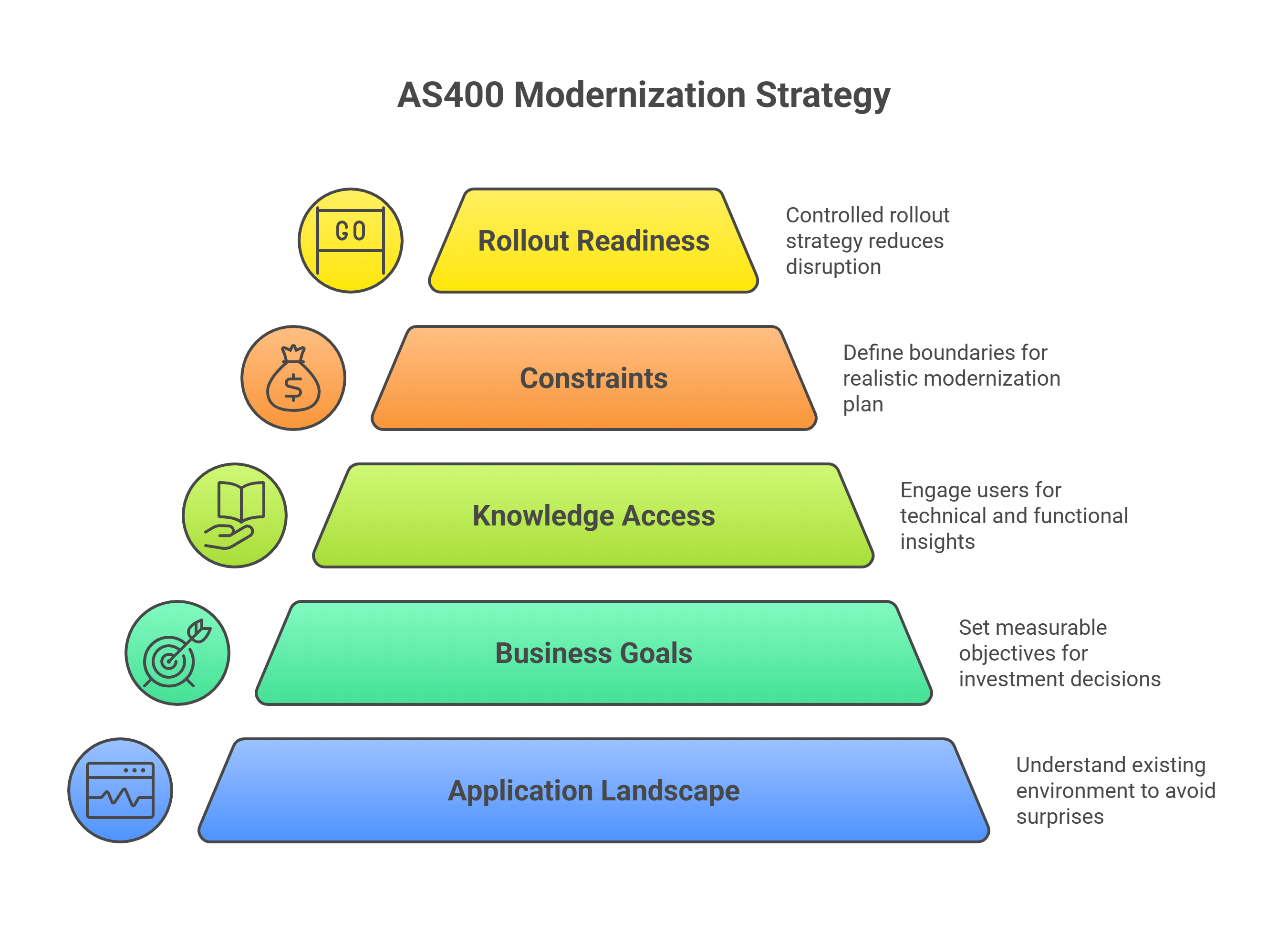
AS400 Application Modernization Methods
Modernizing your AS400 application is not a one-size-fits-all process. The right path depends on the system’s current challenges, the organization’s long-term business goals, and the budget you can realistically allocate. Over the years, we’ve seen four modernization approaches work consistently well. Each takes a different route, from minimal disruption to full redesign, depending on the outcome you want to achieve.
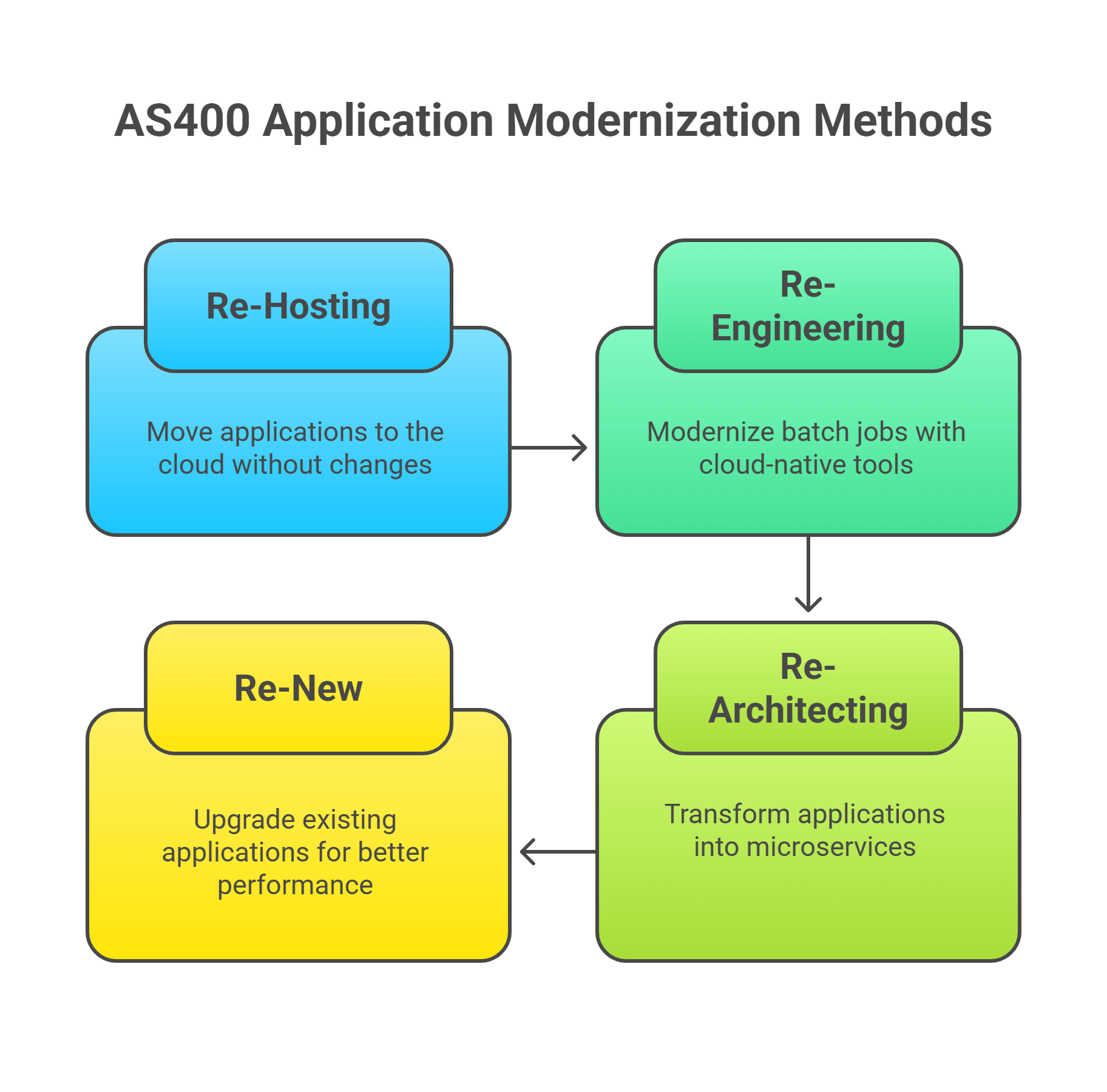
1. Re-Hosting (Lift-and-Shift)
Re-hosting is the fastest and least invasive route. It involves moving your AS400 applications exactly as they are to a cloud environment, using an emulator to replicate the original platform’s behavior.
The application logic, interface, and workflows remain unchanged, but you gain cloud benefits like cost efficiency, better disaster recovery, and easier scaling.
A typical lift-and-shift starts by running RPG or COBOL programs on virtual machines in AWS, Azure, or IBM Cloud using an AS400 emulator such as Infinite i.
The Db2/400 database is migrated in full, along with related services like message queues, schedulers, and reporting tools. Because the application itself isn’t altered, users experience no disruption.
One global oil and gas company moved its AS400 ERP and Db2 database to AWS using an emulator like Infinite i to cut high infrastructure costs, overcome scalability limits, and improve disaster recovery.
The lift-and-shift preserved all workflows, enabled on-demand scaling, and opened integration with modern cloud services, all with minimal disruption. While legacy technical debt remained, the quick, low-risk migration delivered immediate cost savings and flexibility, setting the stage for deeper modernization later.
2. Re-Engineering (Batch Jobs and Process Modernization)
Re-engineering takes aim at one of the biggest pain points in legacy AS400 environments: slow, batch-based data processing. Instead of running overnight ETL jobs, EDI transfers, or reporting cycles, these workloads are migrated to modern cloud-native data platforms that can handle them in near real time.
The process usually starts with identifying which batch jobs are slowing the business down. These are then moved to big data and streaming tools like Hadoop, Apache Spark, Hive, or cloud-based event hubs.
Processed data can be stored in cloud databases or data lakes such as AWS S3 or Azure Data Lake for analytics and reporting. Adding streaming services like Apache Spark Streaming turns what used to be end-of-day reporting into live, actionable dashboards.
A healthcare supply chain company modernized its AS400 batch jobs by moving file-based processing to a cloud data lake and shifting to streaming analytics. Physical batch outputs were stored in AWS S3 for fast access and processed using tools like Hadoop and Apache Spark, while real-time data streams were analyzed with Apache Spark Streaming. This delivered live dashboards for warehouse and supply chain visibility, improved forecasting accuracy, and enabled rapid responses to disruptions.
3. Re-Architecting (Cloud-Native, Microservices-Based Design)
For organizations looking to future-proof, re-architecting offers the most transformative results. This means breaking apart the monolithic AS400 application and rebuilding it as a collection of microservices, containerized workloads, and serverless functions that run natively in the cloud.
A re-architecture project often begins by decomposing large programs into smaller, independent services that can run on AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, or similar platforms. Containers (Docker, orchestrated with Kubernetes) handle workloads that need persistent execution.
Message queues such as Apache Kafka are introduced to decouple services and improve resilience. Data moves to managed cloud databases like Amazon Aurora or Azure SQL, while analytics are powered by cloud data lakes. AI and machine learning services like IBM Watson or Wipro HOLMES can then be integrated directly for automation and predictive insights.
One enterprise re-architected its AS400 monolith into cloud-native microservices on Azure, using Azure Functions for serverless workloads, Docker and Kubernetes for container orchestration, and Apache Kafka for event-driven communication. Data was migrated to Azure SQL and Cosmos DB, while AI and analytics were powered by cloud data lakes and services like Wipro HOLMES. The transformation enabled rapid feature releases, on-demand scalability, greater resilience, and real-time insights through advanced analytics and AI integration.
Get a Tailored AS400 Modernization Plan