The manufacturing industry is largely driven by manual processes. The ‘manual way’ of conducting operations was not just approved but also profitable (ostensibly). And manufacturers were doing quite well, never suspecting the disaster brewing underneath. Come 2020, a catastrophe struck, and struck hard, exposing the fundamental vulnerabilities of the industry in ways transcending the worst nightmare.
A recent study suggests that 72% of companies would adopt RPA to reduce costs and the average transaction handling time, boost productivity, and improve compliance management.
Above anything else, the Covid-19 pandemic disillusioned the world with the erstwhile ‘solid’ manual operations and penalized it for the lack of foresight in the context of technology. The crisis hit manufacturers where it hurts the most; with the majority of the employees confined to their homes, most units simply couldn’t take stock of things and were merely passive observers.
While other industries such as IT and banking were successfully negotiating the economic impacts of the pandemic, manufacturers played a waiting game. With operations coming to a halt, blocking revenue streams, uncertainty about the future only made matters worse. The lack of automation technology was felt more intensely than ever; the few who had embraced it before it was too late, found themselves in a visibly better state of affairs.
The Robotic Process Automation Market is estimated to touch USD 2,467.0 million by 2022.
Automation and Manufacturing: What’s the Equation?
The nature of manufacturing processes makes them strong candidates for automation. When subjected to robotic process automation (RPA), manufacturing units can realize unprecedented levels of productivity with error-free and streamlined procedures. The following use cases drive the point home.
Bill of Materials
For the concerned employee, a bill of material is important but not exciting. The long list of materials, components, sub-components, and other features that make up the BOM deserve the blame. They make the process tedious as employees have to sift through various documents and records to get the necessary details to create a typical BOM.
Why automate?
The BOM impacts the procurement of raw materials, stock monitoring, and the assembly process on the shop floor. An inaccurate BOM can wreak financial and operational havoc in the form of revenue loss.
Why choose RPA:
- RPA can cut down on the spreadsheets and paperwork used to manage the BoM system, making the process more agile.
- Bots can configure automatic alerts for workflow changes, eliminating instances of overstocking and consignment delays.
- RPA can be used to automate data entry and storage; bots can read information from documents and process it as per the configuration.
- Bots can enhance the process by replicating the steps that a human does for generating a BOM while adhering to all regulations.
Advantage: Accurate information that translates into better purchase and expense decisions.
Purchase Order and Invoicing
Purchase order creation and invoicing are among the less fulfilling jobs, but there are no substitutes as yet. Manufactures have forever been in the pursuit of a permanent fix for these resource-hungry tasks but haven’t met with anything that resembles success. PO and invoicing processes encounter frequent issues, impacting other parts of the operation and causing down-time. Add absenteeism, late arrivals, and loss of employee resources to the mix, and business loss seems inevitable.
A study claims that automation brings about a 34% reduction in required resources for invoice processing, 43% for order-to-cash processes, and 32% for vendor management.
Why automate?
Purchase orders and invoices are used for tracking expenses, validate delivery reports, and even in financial audits. One common denominator of these tasks is that they are rule-based, consistent, and template-driven. RPA can ensure unsurpassable accuracy in executing them, enabling the human workforce to focus on other value-adding activities.
Why choose RPA:
- Bots can scan invoices that arrive in the paper, electronic files, PDF, or other forms and transfer the relevant data to the accounting system, ready for matching.
- RPA can send invoices and purchase orders to the concerned department for approvals; bots can send notifications to the stakeholders about the approval status of the PO/invoice.
- Bots can cross-check invoices and purchase orders and identify duplicate records. They can improve compliance with automatic alerts to the PO creator.
- RPA can evaluate and compare order data with the vendor master report and generate POs based on priority.
Advantage: Significantly reduced turnaround time, leading to optimum stock levels of raw material, and hence unhindered operations.
Vendor Management
A typical manufacturing unit usually has high a dependency on suppliers, transporters, and vendors, among others. The sheer complexity and volume of transactions with these external stakeholders make them error-prone. The transactions have fundamentally been human-to-human, and the need for automation, although a desire, has hardly been pursued to help drive business growth.
Why automate?
Most tasks comprising vendor management, including vendor selection and vendor information management, consist of manual activities like preparing requests, sending communications, and evaluating vendor credits. These are rule-based and hence automatable; RPA can streamline them and lead to healthy client-vendor equations.
Why choose RPA:
- Bots can simplify the vendor selection process by automating request preparation, communications, vendor information storage, and vendor credit evaluation.
- Bots can tighten up logistics operations by preparing, reading, sharing, and storing the bill of lading, proof-of-delivery, invoices, shipment tracking, etc.
- Expedite partner onboarding by auto-processing documents received in multiple formats, verifying the requirements quickly, and establishing an automated approval workflow.
- Evaluate the performance of third-party partners with measurable KPIs and identify the areas of improvement.
Advantage: RPA enhances the client-vendor relationship by flagging areas that need attention; bots mitigate risks by establishing close coordination with external stakeholders.
ERP Automation
The ERP system is the lifeline of manufacturers. It’s used to monitor and track various operational processes through real-time information on finances, sales, inventory, and others. The problem is that most manufacturers are still on legacy solutions that involve a high degree of manual intervention. RPA is a tried and tested option to streamline ERP processes for better efficiency.
Why automate?
RPA can be integrated with the ERP to eliminate labor-intensive tasks such as data entry, report generation, and others. Since ERP operators have to deal with a high inflow of operational data, the chances of errors are high, making RPA a no-brainer in the manufacturing ecosystem.
RPA can be implemented to reduce labor-intensive tasks by 80%.
Why choose RPA:
- Automate the generation and sharing of reports on inventory, accounts payable/ receivable, expenses and pricing, and others.
- Monitor critical information related to the ERP’s health by identifying any abnormal behavior or anomaly that is not in accordance with the ERP’s compliance checkpoints.
- Automate data exchange between the organization’s CRM and ERP solutions while ensuring high accuracy.
- Integrate the ERP solution with third-party systems for unhindered monitoring of order status, shipment location, and others.
Advantage: With an RPA-powered ERP, it’s easy for manufacturers to scale operations effortlessly.
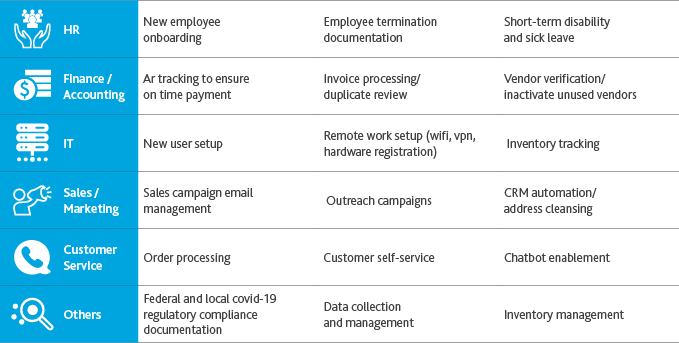
Figure: A few other applications of RPA in the manufacturing sector
RPA is Relief that Manufacturers Need
The Covid-19 pandemic has landed a massive blow to the manufacturing industry. With remote working practices not prevalent in the domain, manufacturers experienced a significant revenue drop and had to resort to stringent cost-cutting measures to ensure survival. This is where RPA could prove to be their savior.
A study has found that about 50% of businesses in the world will increase their RPA Adoption owing to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Cost savings: RPA can significantly boost the output quality of processes, enabling the human workforce to shift focus to higher-value tasks, triggering substantial cost savings.
Speed: At a time when social distancing protocols are in force, RPA can enable employees to cut down on the need to spend long hours in factories by expediting administrative processes and eliminating manual, repetitive tasks.
Employees spend between 10%-25% of their working time on repetitive computer tasks.
Going virtual: With businesses forced to reduce in-person work, manufacturers should leverage RPA to facilitate effective remote work. RPA can help the IT team to expedite the remote work setup process and ensure that employees have access to appropriate connectivity at home.
Business continuity: RPA is also being used by manufacturers to evaluate the current health and COVID-19 risks of employees. Bots can pull employee survey responses to determine if an individual is low risk enough to go to the workplace, helping prevent risks of infection in the workplace.
Count on Nalashaa’s custom RPA solutions
Over the years, our tailored RPA solutions have helped countless manufacturing businesses to inject efficiency into their operations. Our focus has always been to reduce the client’s reliance on the human workforce by deploying automation that expedites workflows and eliminates errors. Even during the Covid-19 disaster, when most manufacturing units were forced to suspend operations, we enabled our clients to ensure business continuity by boosting their remote work structure. We can do the same for you.

